Embroidery digitizing might seem intimidating at first, but with the right tools and techniques, anyone can learn to create beautiful custom designs. Whether you want to stitch a company logo, personalize a gift, or start an embroidery business, this beginner's guide will walk you through everything you need to know about custom digitizing.
What Is Custom Digitizing?
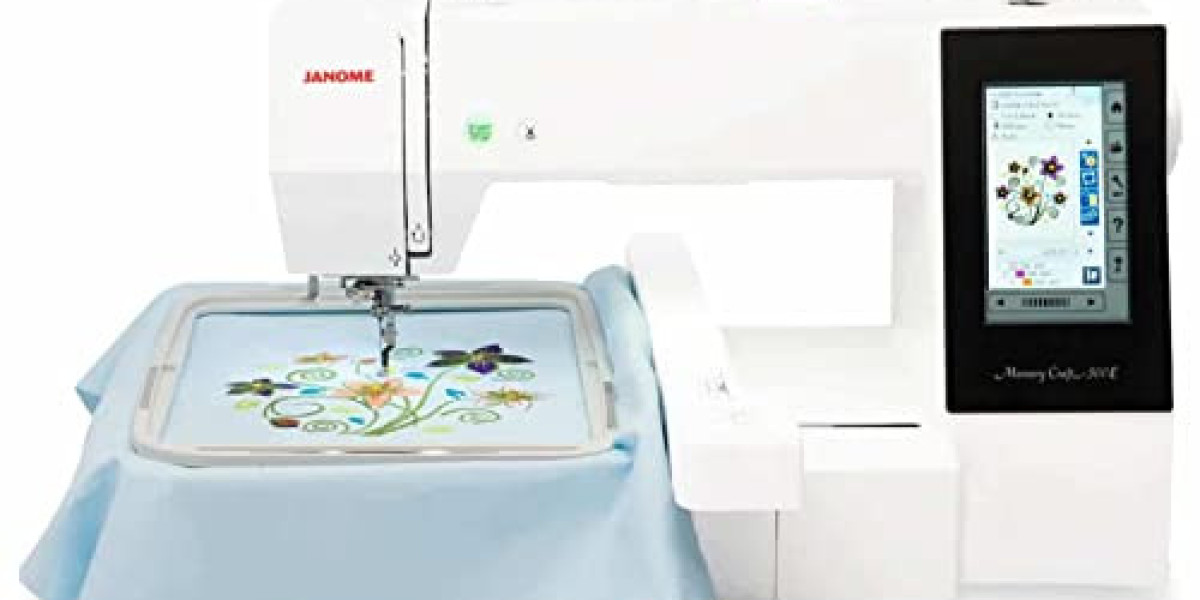
Custom digitizing is the process of converting artwork into a digital embroidery file that machines can read. Unlike auto-digitizing (where software makes all the decisions), custom digitizing gives you complete control over:
Stitch types (satin, fill, running)
Stitch direction and density
Thread color changes
Underlay patterns
This manual approach creates higher quality results than auto-digitizing, especially for complex designs.
Why Learn Custom Digitizing?
Better Quality - Your designs will look more professional
More Creative Control - Bring your exact vision to life
Cost Savings - No need to pay for professional digitizing
Business Potential - Offer digitizing services to others
Essential Digitizing Tools for Beginners
You don't need expensive equipment to start. Here's what to get:
Software Options
Free/Budget Choices:
Ink/Stitch (free Inkscape extension)
SewArt (affordable auto-digitizing with manual controls)
Embrilliance Essentials
Professional Options:
Hatch Embroidery
Wilcom EmbroideryStudio
Pulse Ambassador
Hardware Recommendations
Any standard computer (Windows or Mac)
A graphics tablet helps but isn't required
Your embroidery machine for testing
Step-by-Step Digitizing Process
Follow this workflow to digitize your first design:
1. Prepare Your Artwork
Start with high-contrast, simple images
Vector files (AI, EPS) work best
Clean up JPG/PNG files in Photoshop first
2. Set Up Your File
Choose the right hoop size
Set your design dimensions
Establish center points and registration marks
3. Create the Outline
Use running stitches for fine details
Convert to satin stitches for borders
Adjust stitch length (1.5-3mm is typical)
4. Add Fill Areas
Select appropriate fill patterns
Set stitch angle (30-60° works for most fabrics)
Add underlay stitches for stability
5. Refine Your Design
Check stitch density (adjust for fabric type)
Optimize color changes
Add tie-off stitches where needed
6. Test and Adjust
Stitch out on similar fabric
Note any puckering or gaps
Return to software to refine
5 Beginner Mistakes to Avoid
Too Many Stitches - Causes thread breaks and fabric distortion
Ignoring Underlay - Leads to poor registration and loose stitches
Wrong Stitch Types - Using fill where satin would work better
Overlooking Pull Compensation - Accounts for fabric stretch
Skipping the Test Stitch - Always test before final production
Practice Projects to Build Skills
Start with these simple designs:
Basic monogram (practice satin stitches)
Simple shape like a heart (learn fill stitches)
Two-color logo (master color changes)
Text phrase (understand letter spacing)
Where to Find Learning Resources
YouTube tutorials (search your software name + "tutorial")
Facebook digitizing groups
Software company training webinars
Local embroidery shop classes
Taking Your Skills to the Next Level
Once you've mastered basics:
Experiment with specialty threads
Try 3D puff techniques
Learn multi-hoop designs
Offer digitizing services locally
Final Thoughts
Custom digitizing is a learnable skill that opens up endless creative possibilities. Start simple by learning how to Convert Image to Embroidery File, be patient with your progress, and remember - every professional digitizer was once a beginner too. With regular practice of both custom digitizing and image conversion techniques, you'll soon be creating embroidery files you're proud to stitch out.